

Pairs Æ Exploration Direct the students to the appropriate link for the GSP® activity. Note: the scales on the graphs are all 1:1 unless stated otherwise. Students weak in transformations should be given the quadratic transformations. Photocopy BLMs – different colour for each function, cut and placed in envelopes One group member shares with the whole class.

Groups summarize the similarities of the transformation notation regardless of the function type. Each member of the group takes the three pieces of a match and finds members of the other groups that have the same transformation. Students match the equation, the graph, and the written description of the transformation. Provide each group with an envelope containing the squares of one type of function from BLM 5.10.1. ħ5 min Assessment Opportunities Minds On… Groups of 5 Æ Activating Prior Knowledge.Connect prior knowledge of transformations in order to graph logarithmic functions.Math Learning Goals Investigate the roles of the parameters d and c in functions of the form y = log10 ( x − d ) + c and the roles of the parameters a and k in functions of the form y = a log10 ( kx ). (lesson not included) Jazz Summative Assessment (lesson not included) Log or Rhythm GSP® file: Log Investigation Solve problems of exponential or logarithmic equations algebraically arising from real world applications. Ĭonnect prior knowledge of transformations in order to graph logarithmic functions. Investigate the roles of the parameters d and c in functions of A2.3 the form y = log10 ( x − d ) + c and the roles of the parameters a CGE 2c and k in functions of the form y = a log10 ( kx ). Solve exponential equations by using logarithms. Solve exponential equations by finding a common base. Pose and solve problems using given graphs or graphs generated with technology of logarithmic and exponential functions arising from real world applications. TIPS4RM: MHF4U: Unit 5 – Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Solve problems that demonstrate the property of exponential functions that the instantaneous rate of change at a point of an exponential function is proportional to the value of the function at that point. Solve problems involving average and instantaneous rates of D1.4–1.9 change using numerical and graphical methods for exponential and logarithmic functions. Use the laws of logarithms to simplify and evaluate logarithmic expressions. Recognize equivalent algebraic expressions involving logs and exponents. Explore the graphs of a variety of logarithmic and exponential expressions to develop the laws of logarithms. Using technology, graph implicitly, logarithmic functions with different bases to consolidate properties of logarithmic functions and make connections between related logarithmic and exponential equations (e.g., graph x = a y using Winplot or Graphmatica or graph a reflection in y = x using GSP®).Įxplore graphically and use numeric patterning to make connections between the laws of exponents and the laws of logarithms. Define the logarithm of a number to be the inverse operation of exponentiation, and demonstrate understanding considering numerical and graphical examples. Solve simple exponential equations, by rewriting them in logarithmic form.Įxplore and describe key features of the graphs of exponential functions (domain, range, intercepts, increasing/decreasing intervals, asymptotes). Approximate the logarithm of a number with respect to any base with technology. Make connections between related logarithmic and exponential equations. Investigate the relationship between y = 10 x and y = b x and how A1.1, 1.2, 1.3 they relate to y = log x and y = logb x. solve problems that can be modeled using exponential or logarithmic functions.evaluate exponential and logarithmic expressions and equations.identify features of the logarithmic function including rates of change.
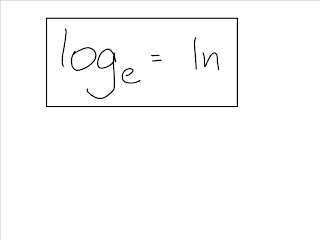
simplify exponential and logarithmic expressions using exponent rules.develop the understanding that the logarithmic function is the inverse of the exponential function.Lesson Outline Big Picture Students will: Unit 5: Exponential and Logarithmic Functions


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
